Feb 6 First Look Overview
Now that we have a base knowledge of the anatomy and function of the Lymphatic System, it’s time to do an overview of the entire system in action.
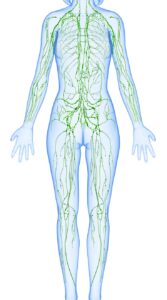
Review of Lymphatic System Function
- Collecting excess fluid from your body’s tissues and returning it to your bloodstream.
- Helping your body absorb fats.
- Protecting your body against invaders
Structure
The organs of the lymphatic system are your:
- Bone marrow.
- Thymus.
- Lymph nodes.
- Spleen.
- Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT).
- Lymph. Lymph, also called lymphatic fluid, is a collection of the extra fluid that drains from cells and tissues in your body and isn’t reabsorbed into your capillaries. Lymph contains many different substances, including proteins, minerals, fats, damaged cells, cancer cells and germs. Lymph also transports infection-fighting white blood cells (lymphocytes).
- Lymphatic vessels.
- Collecting ducts.
- Tonsils and adenoids.
